

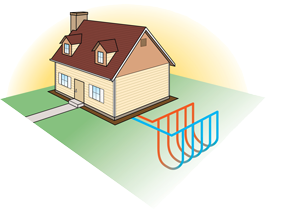
Geothermal heating and cooling systems are more energy efficient than conventional air conditioners, gas furnaces, and air source heat pumps. Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground source heat pumps, take advantage of the mild temperatures below the earth's surface, moving heat from the earth into the house during winter, and moving heat from the house into the earth during summer.
In the summer, the temperature deep in the earth is usually much cooler than the surrounding air. A geothermal heat pump rejects heat from the house into the relatively cool earth rather than into the hot summer air. Moving heat into the cool earth requires less energy than moving heat into hot air, making the geothermal heat pump more efficient.
In the winter, the earth is usually much warmer than the surrounding air. A geothermal heat pump extracts heat from the relatively warm earth rather than extracting heat from the cold winter air. Extracting heat from the warm earth requires less energy than extracting heat from cold air, making the geothermal heat pump more efficient. Air source heat pumps become even more inefficient when they ice up in the winter and must undergo defrost cycles. Properly designed geothermal systems work fine in the coldest weather.